India currently comprises 28 states and 8 union territories. Each state has its own government, led by a Chief Minister, while union territories are governed directly by the Central Government, with some having a Lieutenant Governor. The division of states and union territories reflects India’s diverse cultural and linguistic landscapes.
Overview of Indian States
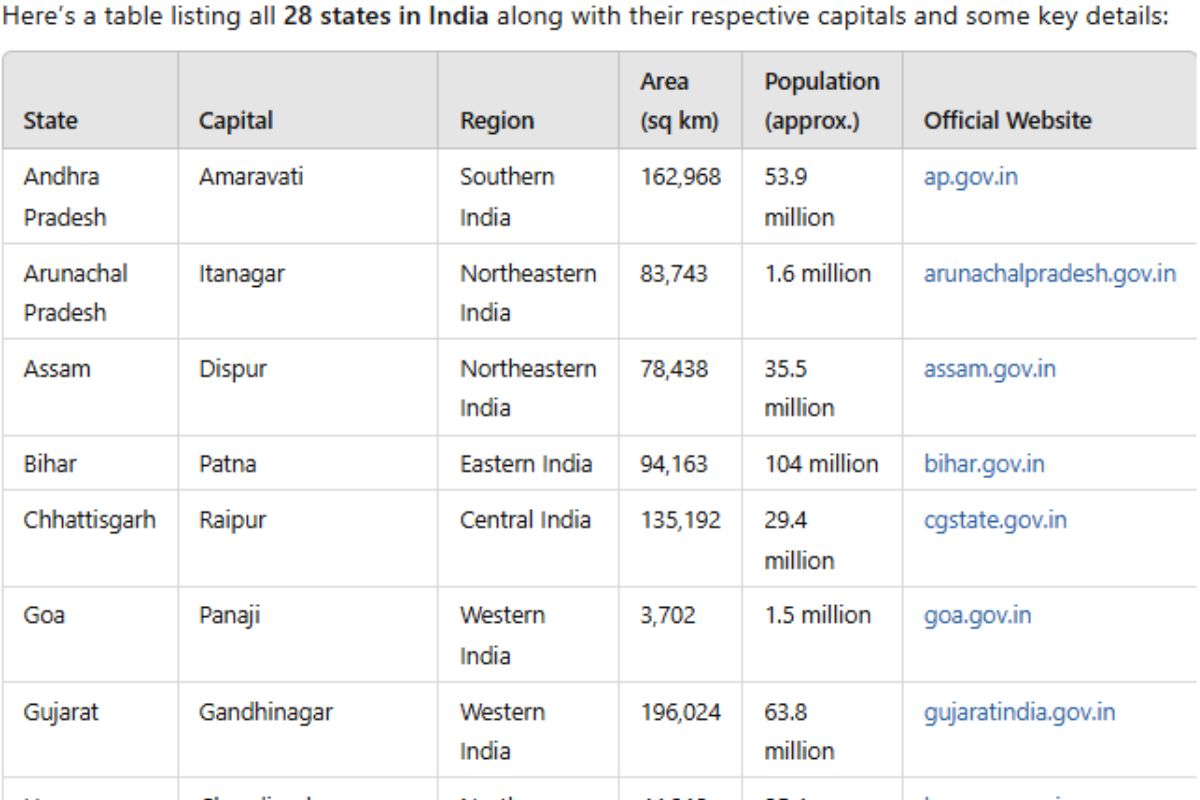
Here’s a table listing all 28 states in India along with their respective capitals and some key details:
| State | Capital | Region | Area (sq km) | Population (approx.) | Official Website |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andhra Pradesh | Amaravati | Southern India | 162,968 | 53.9 million | ap.gov.in |
| Arunachal Pradesh | Itanagar | Northeastern India | 83,743 | 1.6 million | arunachalpradesh.gov.in |
| Assam | Dispur | Northeastern India | 78,438 | 35.5 million | assam.gov.in |
| Bihar | Patna | Eastern India | 94,163 | 104 million | bihar.gov.in |
| Chhattisgarh | Raipur | Central India | 135,192 | 29.4 million | cgstate.gov.in |
| Goa | Panaji | Western India | 3,702 | 1.5 million | goa.gov.in |
| Gujarat | Gandhinagar | Western India | 196,024 | 63.8 million | gujaratindia.gov.in |
| Haryana | Chandigarh | Northern India | 44,212 | 25.4 million | haryana.gov.in |
| Himachal Pradesh | Shimla | Northern India | 55,673 | 7.3 million | himachal.nic.in |
| Jharkhand | Ranchi | Eastern India | 79,716 | 32.9 million | jharkhand.gov.in |
| Karnataka | Bengaluru | Southern India | 191,791 | 68.6 million | karnataka.gov.in |
| Kerala | Thiruvananthapuram | Southern India | 38,863 | 35.7 million | kerala.gov.in |
| Madhya Pradesh | Bhopal | Central India | 308,350 | 72.6 million | mp.gov.in |
| Maharashtra | Mumbai | Western India | 307,713 | 124 million | maharashtra.gov.in |
| Manipur | Imphal | Northeastern India | 22,327 | 3.1 million | manipur.gov.in |
| Meghalaya | Shillong | Northeastern India | 22,429 | 3.3 million | meghalaya.gov.in |
| Mizoram | Aizawl | Northeastern India | 21,081 | 1.1 million | mizoram.gov.in |
| Nagaland | Kohima | Northeastern India | 16,579 | 2.2 million | nagaland.gov.in |
| Odisha | Bhubaneswar | Eastern India | 155,707 | 42 million | odisha.gov.in |
| Punjab | Chandigarh | Northern India | 50,362 | 30 million | punjab.gov.in |
| Rajasthan | Jaipur | Northern India | 342,239 | 78.3 million | rajasthan.gov.in |
| Sikkim | Gangtok | Northeastern India | 7,096 | 0.6 million | sikkim.gov.in |
| Tamil Nadu | Chennai | Southern India | 130,058 | 77 million | tn.gov.in |
| Telangana | Hyderabad | Southern India | 112,077 | 39.3 million | telangana.gov.in |
| Tripura | Agartala | Northeastern India | 10,491 | 3.6 million | tripura.gov.in |
| Uttar Pradesh | Lucknow | Northern India | 243,290 | 231 million | up.gov.in |
| Uttarakhand | Dehradun (Winter) / Gairsain (Summer) | Northern India | 53,483 | 11 million | uttarakhand.gov.in |
| West Bengal | Kolkata | Eastern India | 88,752 | 100 million | wb.gov.in |
Regional Breakdown of States
India’s states are categorized into various regions based on cultural, linguistic, and geographic characteristics:
- Northern India: Includes states like Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, and Himachal Pradesh.
- Western India: Maharashtra, Gujarat, Rajasthan, and Goa are prominent states in this region.
- Southern India: Known for states like Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh.
- Eastern India: Includes states such as West Bengal, Bihar, Odisha, and Jharkhand.
- Northeastern India: Comprising Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, Tripura, and Arunachal Pradesh.
- Central India: Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh form this region.
States by Population and Area
Indian states vary significantly in population and size. For instance:
- Largest State by Area: Rajasthan
- Smallest State by Area: Goa
- Most Populated State: Uttar Pradesh
- Least Populated State: Sikkim
Union Territories of India
India’s 8 union territories have unique administrative setups. Some are culturally significant regions, while others hold strategic importance for defense and international trade.
Unique Features of Union Territories
Union territories like Delhi and Puducherry enjoy partial statehood with elected legislative assemblies, while others like Andaman and Nicobar Islands and Lakshadweep are directly governed by the Central Government.
Differences Between States and Union Territories
- Governance: States have their own legislative governments; union territories are centrally governed.
- Administration: Union territories are administered by appointed administrators or Lieutenant Governors.
- Autonomy: States possess more legislative power than union territories, with certain UTs having minimal autonomy.
Current State Count and Changes Over Time
Formation and Reorganization of States
Since India’s independence in 1947, there has been significant reorganization of states to better align with linguistic and administrative needs. For example, states like Maharashtra and Gujarat were created in 1960, and Telangana was carved out from Andhra Pradesh in 2014.
Notable Recent Changes
- 2014: Telangana became the 29th state of India.
- 2019: Jammu and Kashmir was restructured into two separate union territories – Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh.
Table of Indian States and Union Territories with Key Information
| Region | State/Union Territory | Capital | Area (sq km) | Population | Contact Email | Website |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northern India | Uttar Pradesh | Lucknow | 243,290 | 199.8 million | contact@up.gov.in | up.gov.in |
| Western India | Maharashtra | Mumbai | 307,713 | 112.4 million | cm@maharashtra.gov.in | maharashtra.gov.in |
| Southern India | Tamil Nadu | Chennai | 130,058 | 72.1 million | cmcell@tn.gov.in | tn.gov.in |
| Eastern India | West Bengal | Kolkata | 88,752 | 91.3 million | chiefsec@wb.gov.in | wb.gov.in |
| Central India | Madhya Pradesh | Bhopal | 308,252 | 72.6 million | cm@mp.gov.in | mp.gov.in |
| Union Territories | Delhi | New Delhi | 1,484 | 16.7 million | contact@delhi.gov.in | delhi.gov.in |
| Jammu and Kashmir | Srinagar/Jammu | 55,673 | 12.5 million | admin@jk.gov.in | jk.gov.in |
Frequently Asked Questions on Indian States and UTs
- What is the total number of states in India?
- India has 28 states and 8 union territories as of 2024.
- Which is the largest state in India by area?
- Rajasthan holds the title as the largest state by area.
- What’s the difference between a state and a union territory?
- States have more legislative powers and autonomy, while union territories are centrally administered, with limited self-governance.
- What recent changes have occurred in the state count?
- In 2019, Jammu and Kashmir were split into two union territories: Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh.
Conclusion
India’s 28 states and 8 union territories offer a kaleidoscope of cultures, languages, and histories. This division into states and union territories not only ensures effective administration but also preserves India’s unique cultural heritage. The geographical, economic, and demographic diversity of these regions makes India one of the most colorful and complex countries in the world.