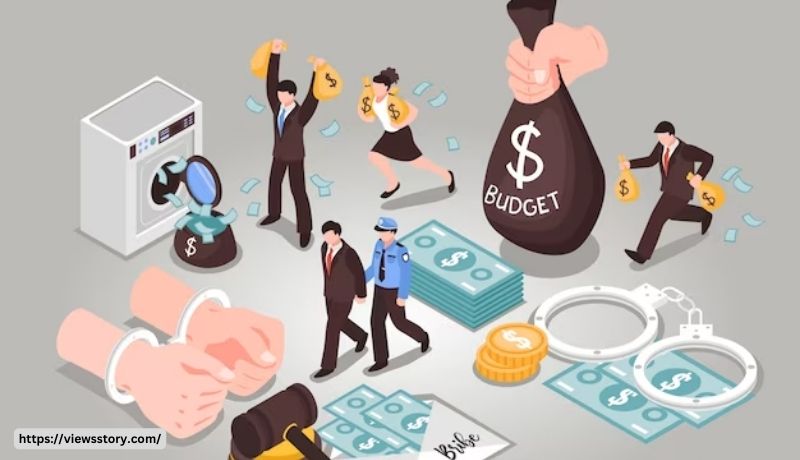
Money laundering is a term that often appears in news headlines and crime dramas, but what exactly does it mean? In simple terms, money laundering is a process that criminals use to make illegally gained money appear legitimate. In this blog, we’ll dive into the details of what money laundering is and how it works.
The Basics:
Imagine you’re a thief, and you’ve just stolen a large amount of cash. You can’t simply deposit this money into a bank because the bank would ask questions about where it came from. So, you need to make it look like this money was earned legally. This is where money laundering comes into play.
The Stages of Money Laundering:
Money laundering involves several stages to make “dirty” money clean. These stages are:
- Placement: At this stage, the criminals introduce their ill-gotten gains into the financial system. They might break the large sum into smaller amounts to avoid suspicion, or they could use it to purchase valuable assets like cars, jewelry, or real estate. These assets can be easily resold later.
- Layering: In this stage, the goal is to make it hard for authorities to trace the origin of the money. Criminals might transfer funds between different accounts, engage in complex financial transactions, or even move money across borders to different jurisdictions. The idea is to create a web of transactions that obscures the source.
- Integration: Finally, the money is reintroduced into the economy as “clean” funds. This could happen by selling the assets purchased earlier, investing it in legal businesses, or simply by depositing it into a bank. At this point, the money looks like legitimate earnings.
Also Read : UnitedHealthcare Community Plan
Why is Money Laundering a Problem?
Money laundering is a big problem for several reasons:
- Supporting Criminal Activities: Money laundering allows criminals to profit from their illegal activities, making it easier for them to continue doing harm.
- Destabilizing Economies: It can affect the stability of economies and financial institutions. Illegally obtained money can distort markets and lead to economic imbalances.
- Tax Evasion: Money launderers often avoid paying taxes on their ill-gotten gains, which deprives governments of revenue needed for public services.
- Corruption: Money laundering can foster corruption within banks, businesses, and even governments as individuals and organizations become complicit in the process.
How is Money Laundering Combated?
Governments and financial institutions worldwide have taken significant steps to combat money laundering. These include:
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Laws: Many countries have established AML laws that require financial institutions to monitor and report suspicious transactions.
- Know Your Customer (KYC) Regulations: These regulations require banks and financial institutions to verify the identity of their customers, making it harder for criminals to use the financial system.
- International Cooperation: Money laundering is a global issue, so international organizations like the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) work to set global standards and promote cooperation among countries.
- Advanced Technology: The use of technology, like data analytics and artificial intelligence, has greatly improved the detection of suspicious financial activities.
Also Read : Integrated Communication in Marketing
Different Types of Money Laundering
Money laundering is a complex and diverse activity, and there are various types or methods that criminals use to conceal the origins of their illicitly obtained funds. Here are some common types of money laundering:
- Structuring or Smurfing:
- In this method, individuals or criminals break down large sums of money into smaller, less suspicious amounts. They make multiple small deposits or transactions in a way that avoids drawing the attention of authorities who monitor large transactions.
- Shell Companies:
- Criminals create fake companies, known as shell companies, to make it appear as though their illegal funds are coming from a legitimate business. These companies often exist on paper only and have no real operations.
- Trade-Based Money Laundering:
- This method involves manipulating the prices, quantities, or types of goods in international trade transactions to move money across borders while disguising its true origins. Criminals can overvalue or undervalue goods or engage in fictitious trades to move money.
- Real Estate:
- Criminals invest their illegal funds in real estate, buying properties or assets that can appreciate over time. They can then sell these properties and claim the money as legitimate earnings.
- Cryptocurrency:
- Some criminals use cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin to launder money. Cryptocurrencies offer relative anonymity, making it challenging for authorities to trace transactions. Criminals may move funds through various cryptocurrency wallets to obscure the source.
- Online Gambling:
- Money laundering can occur through online gambling platforms. Criminals may deposit dirty money into online casinos, place bets, and then cash out, making the money appear as gambling winnings.
- Cash-Based Businesses:
- Some illegal businesses, such as underground casinos, bars, or nightclubs, may mix illicit funds with legitimate cash earnings to obscure their origins.
- Hawala System:
- This informal money transfer system is common in some parts of the world. It involves a network of brokers who facilitate the transfer of funds between individuals without physically moving money across borders, making it challenging to trace.
- Layering and Complex Transactions:
- Criminals engage in a series of intricate financial transactions to distance the illegal funds from their source. This might include transferring funds between accounts, buying and selling assets, and routing money through multiple countries.
- Cash Smuggling:
- Criminals physically transport large amounts of cash across borders, often in hidden compartments or concealed in everyday items.
- Art and Collectibles:
- Money launderers might purchase valuable art, antiques, or collectibles and then sell them at auction or through private sales, converting the dirty money into clean assets.
- Front Companies:
- Criminals create seemingly legitimate businesses that appear to generate revenue, but their primary purpose is to receive and legitimize illegal funds.
Conclusion
In conclusion, money laundering is a complex process that allows criminals to legitimize their ill-gotten gains. It’s a significant problem with far-reaching consequences, including supporting criminal activities and destabilizing economies. Governments and financial institutions are working together to combat this issue and protect the integrity of the financial system. Understanding the basics of money laundering is an important step towards preventing and detecting this illegal activity.